
A scientific way to better understand conspiracy theories
This links to an interesting scientific article published in February 2022. The report provides a relevant and updated view on how to handle “conspiracy theories”.
“Findings show that the majority of studies lack a definition of conspiracy theories and fail to conceptually delineate conspiracy theories from other forms of deceptive content. We also found that while the field employs a variety of methodological approaches, most studies have focused on individual, “mainstream” social media platforms, “Western” countries, English-language communication, and single conspiracy theories.”
Conspiracy theories are “alternative explanations of historical or ongoing events claiming that people or groups with sinister intentions are engaged in conspirational plotting have permeated online communication, news media coverage, popular culture and political rhetoric”.
If you have encountered a believer of such theories you will know: A debate with people who believe such theories can be quite stressful – usually it is not a discussion but quickly turns into a war over who is right.
The scientific article explores the evolution of such topics in an online environment and provides an overview of the research on this topic, including recommendations towards future scientific analysis.
“For a long time, conspiracy theories were perceived as harmless phenomena that were “silly and without merit” (Keeley, 1999: 109) or only existed as “‘soft’ beliefs” (Sunstein and Vermeule, 2009: 220) that people quietly kept but rarely acted upon.”
But, especially during the COVID-19 years the world witnessed a rising influence of such views and a high visibility of groups supporting such theories on almost all social networks.
Profound changes in the media and platform ecosystem and particularly the advent of social media platforms, which have enabled faster communication about and dissemination of conspiratorial narratives, have changed this, however. Thus, the last few decades have seen a plethora of “high-profile conspiracy theorizing” (Uscinski, 2018: 233) around topics such as vaccination, climate change, the 9/11 attacks (Mahl et al., 2021), or, most recently, the COVID-19 pandemic (Zeng and Schäfer, 2021).
Source:
Conspiracy Theories in online environments: An interdisciplinary literature review and Agenda for future research
By
Photo by Markus Winkler on Unsplash

How to assess and access your company’s growth potential?
Webinar powered by NGI TETRA and NGI TruBlo.
When: 2 June 2022 | 15:00 CEST
Where: Online
Registration: https://meet.zoho.eu/iBWV0Wuwxw
As your customer base grows and you start to make a profit, it’s only natural to start thinking about your next steps and ask yourself: is it time to scale?
But where to start and what are the next steps to take? Scaling can be full of challenges and premature scaling is considered to be one of the main reasons why young companies fail.
At this webinar we will talk about:
- What are the key questions to ask before scaling?
- What is premature scaling?
- What are the components of a good “ready to scale checklist”?
Speakers
.jpg) Andrej Petrus is investment Manager @ ZAKA – venture capital family office investing primarily in the pre-seed and seed stage (50-500k EUR) in CEE region. Agile generalist with experiences in venture building for CEAi and M&A and Strategy consultancy for PwC in Prague. Assisting the Board of Directors of SLOVCA (Slovak Venture Capital and Private Equity Association) as Project Manager.
Andrej Petrus is investment Manager @ ZAKA – venture capital family office investing primarily in the pre-seed and seed stage (50-500k EUR) in CEE region. Agile generalist with experiences in venture building for CEAi and M&A and Strategy consultancy for PwC in Prague. Assisting the Board of Directors of SLOVCA (Slovak Venture Capital and Private Equity Association) as Project Manager.
LinkedIn
 Donnie Sc Lygonis works as an Innovation Strategist and Business Coach at KTH Innovation, the innovation office at The Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm. He has been working with entrepreneurship and innovation for over 25 years, both running his own companies or helping others start theirs. He is an appreciated speaker on innovation and creativity, having spoken at 5 TEDx events and been part of 3 separate TV-series on innovation.
Donnie Sc Lygonis works as an Innovation Strategist and Business Coach at KTH Innovation, the innovation office at The Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm. He has been working with entrepreneurship and innovation for over 25 years, both running his own companies or helping others start theirs. He is an appreciated speaker on innovation and creativity, having spoken at 5 TEDx events and been part of 3 separate TV-series on innovation.
LinkedIn
KTH Readiness System
You will be introduced to the KTH Readiness System, a unique and effective approach for self-assessment of how far your project has evolved. There are many, many approaches how to getting an idea off the ground and transforming it into a real world. One approach which should be known more widely is the KTH Readiness Level. It is a simple, yet very effective and helpful approach to letting an idea evolve, step by step. The approach comes from the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm (KTH).
Brief overview
Originally developed as a step-by-step development approach for technology at NASA, the KTH Readiness System has extended to seven dimensions that are relevant for every new idea. The key questions are: How ready is your idea to be used by customers, how far evolved are the development steps for the technology, the business model, the IPR, the team and the funding.
Each of these dimensions will be checked against a grade scale, which starts at one and has the highest level at nine. The scales are visualised as thermometers. The visualization is used as a simple tool to enable an assessment of the founders, potential funders and other stakeholders. The system is very simple to use and helps to align the many possible activities of a start-up into a logical build-up process.
For illustration, here are the levels to work on for the business model. The process starts at the bottom, at level 1. In this process, an early, unclear business idea is gradually filled with assumptions, gradually described and then checked for viability through tests with potential clients. Based on the findings there is an added business model, early pricing and projections for revenue.
In total there are six Innovation Readiness Levels:
- Customer Readiness Level (CRL): To confirm customer needs and interest
- Technology Readiness Level (TRL): To develop and test the technology, product, service, or concept
- Business Model Readiness Level (BRL): To establish that the concept can be financially, environmentally, and socially viable and feasible
- IPR Readiness Level (IPRL): To clarify the legal and IP situation and secure relevant IP protection
- Team Readiness Level ( TMRL): To secure the right competencies and align the team
- Funding Readiness Level (FRL): To secure the necessary funding to take the idea to the market
Value and benefits
The KTH Innovation Readiness Level is a tool with many applications that adds value for several users and stakeholders (idea owners, coaches, managers, and external partners). For example:
- Snapshot of status and maturity – use the tool to quickly and without bias assess the maturity and current development status of an idea
- Reality check – the tool enables idea owners to more objectively define their progress across several important dimensions
- Coaching and communication – offering clear and defined terminology and a visual model allow coaches, advisors, and idea owners to communicate effectively around the idea development. It also provides a structure for individual meetings as well as the entire process
- Guidance – the model provides key steps and questions that need to be addressed and gives a clear roadmap for both coaches and idea owners throughout the process
- Portfolio management – the possibility to quantify and visualise the development progress of the ideas in your entire portfolio can generate useful metrics that help your organisation to objectively and fairly allocate resources and in other ways control and guide your innovation support process
The model is built to align with and include the current best practices and well-known methodologies in innovation development such as the lean startup methodology, the business model/lean canvas, etc.
More info:
https://kthinnovationreadinesslevel.com
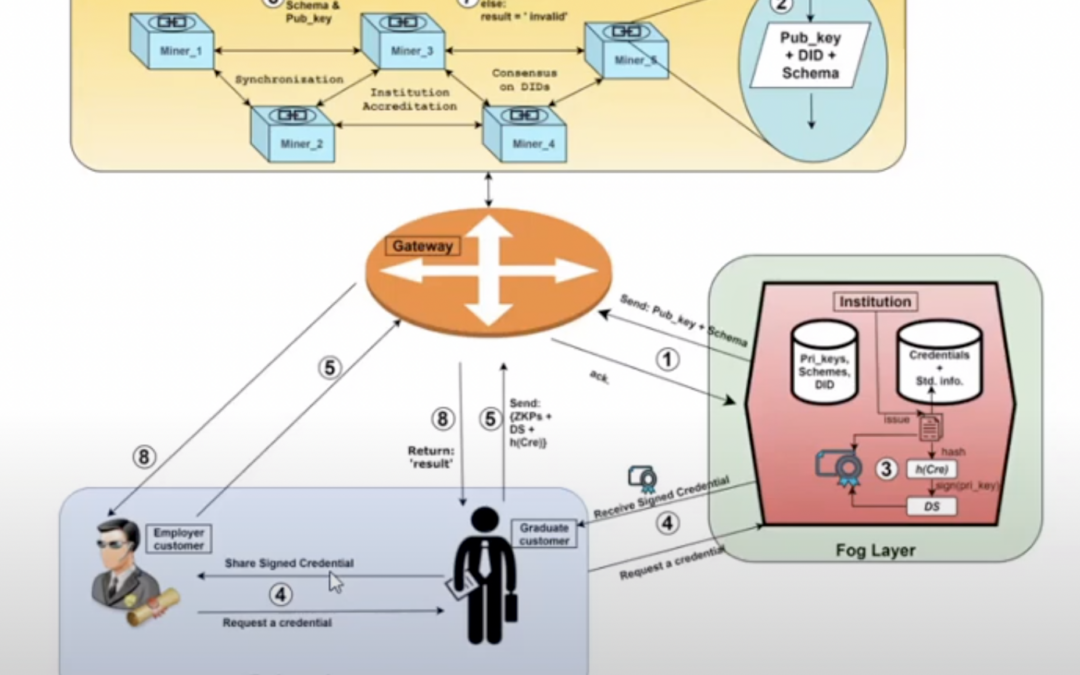
FogBlock4Trust: How to combine global institution accreditation and distributed credential verification
Below is a video demo of the FogBlock4Trust project, which aims at realising a Fog-assisted Blockchain-based credential management solution to strengthen the trust and privacy of users.
Innovation: The most important novelty of FogBlock4Trust is the provision of two distinct major services within one framework, namely global institution accreditation, and distributed credential verification. Other recent proposals for credential management are inefficient, unreliable in terms of storage management and privacy AND/OR provide only one of the two services.
Use case: The FogBlock4Trust solution is planned as a global institution/provider accreditation and credential verification system. It will support the use of one-way encryption, symmetric and asymmetric encryption, digital signatures, Zero-Knowledge-Proofs, and an improved Proof-of-Signature consensus algorithm. Exploiting these methods and technologies for providing end-users with full privacy-preserving distributed accreditation and verification services is the goal of FogBlock4Trust.
Scenario: The assumed scenario for the demo is that there are issuers of online credentials, in a zero-knowledge setting. A real-world example would be a group of universities providing trustable digital copies of certifications from students to each other. Such a setting (a group of issuers, a multitude of certificates/documents, and a large number of single users who can access the system for certain tasks) can be found in a range of domains.
Demo: The 20-minute demo shows how cloud and fog computing can be enhanced with blockchain features.
Team:
Attila Kertesz, Project leader: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Attila-Kertesz-2
Hamza Baniata, Blockchain specialist: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hamza-Baniata
Tamas Pflanzner, Cloud, IoT and Web developer: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tamas-Pflanzner

How can #blockchain help against disinformation?
Please join us on Tuesday, March 29 from 09:45 CET for a TruBlo-themed online event “TruBlo initiatives against disinformation: media and digital technologies” organised and hosted by TruthSeekers’ Chain, a project from the First Open Call of TruBlo.
You will have the chance to hear from ATC about TruBlo (NGI initiative), learn from Deutsche Welle and Thomson Reuters about disinformation and the media industry, and hear from TruBlo teams such as TruthSeekers’ Chain, FAKE, OttCT and TrueBees how they innovate towards trustable content using blockchain technology.
TruthSeekerchain profile: https://www.trublo.eu/truth-seekers-chain/
Homepage of the project: https://truthseekerschain.grupposigla.it/index.html
#digital #technology #blockchain #disinformation #misinformation

DONS: Dynamic Optimized Neighbor Selection for Smart Blockchain Networks (Research)
Below is an abstract of a scientific article, which has been accepted for publication by a prestigious journal. The findings are related and useful for the funded project of the team. Their project in TruBlo is called FogBlock4Trust. Findings from the work below are used in the project.
Authors:
Hamza Baniata, Ahmad Anaqreh, Attila Kertesz
Article:
DONS: Dynamic Optimized Neighbor Selection for Smart Blockchain Networks”, Future Generation Computer Systems
Main points:
- We propose DONS for enhancing Blockchain networks in terms of Finality and Fidelity.
- We propose AnoLE, a privacy-aware method for leader election in public Blockchains.
- DONS showed optimum message propagation in different network models and sizes.
- Our methods provide high security and privacy measures compared to current methods.
Abstract:
Blockchain (BC) systems mainly depend on the consistent state of the Distributed Ledger (DL) at different logical and physical places of the network. The majority of network nodes need to be enforced to use one or both of the following approaches to remain consistent:
- (i) to wait for certain delays (i.e. by requesting a hard puzzle solution as in PoW and PoUW, or to wait for random delays as in PoET, etc.)
- (ii) to propagate shared data through the shortest possible paths within the network.
The first approach may cause higher energy consumption and/or lower throughput rates if not optimized, and in many cases, these features are conventionally fixed. Therefore, it is preferred to enhance the second approach with some optimization.
Previous works for this approach have the following drawbacks: they may violate the identity privacy of miners, only locally optimize the Neighbor Selection method (NS), do not consider the dynamicity of the network, or require the nodes to know the precise size of the network at all times.
In this paper, we address these issues by proposing a Dynamic and Optimized NS protocol called DONS, using a novel privacy-aware leader election within the public BC called AnoLE, where the leader anonymously solves the “The Minimum Spanning Tree” problem (MST) of the network in polynomial time.
Consequently, miners are informed about the optimum NS according to the current state of network topology. We analytically evaluate the complexity, security and privacy of the proposed protocols against state-of-the-art MST solutions for DLs and well-known attacks. Additionally, we experimentally show that the proposed protocols outperform state-of-the-art NS solutions for public BCs. Our evaluation shows that the proposed DONS and AnoLE protocols are secure, private, and they acutely outperform all current NS solutions in terms of block finality and fidelity.

Fig. 1. Phases and steps of the proposed DONS protocol. Each step is performed by one (or more) system entity(s).
A step may depend on the result of a preceding step of the current round, or on the result of a subsequent step of the previous round.
Full paper:
DONS: Dynamic Optimized Neighbor Selection for Smart Blockchain Networks”, Future Generation Computer Systems, Volume 130, May 2022, Pages 75-90 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.12.010
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivatives License (CC BY NC ND).

